Students who listen to this Grade 2 Core Knowledge History and Geography unit discover that Americans had a difficult task at hand after winning the Revolutionary War: they had to figure out a better way to govern themselves. Such leaders as James Madison, George Washington, Alexander Hamilton, and Benjamin Franklin traveled to Philadelphia to meet at the Constitutional Convention, with the goal of creating a new government. Students learn that the talks were held in secret in Independence Hall and that American leaders argued about many issues until they agreed to approve a new Constitution. They then hear that James Madison (whom we call the Father of the Constitution), along with John Jay and Alexander Hamilton, wrote the Federalist Papers to explain the document’s merits and to persuade the states to vote for it. Students find out that the states did finally approve the Constitution; that Madison wrote a Bill of Rights that was added to it; that the Constitution gives the American people the right to decide what the laws should be for our country; and that we can still amend it today.(5 lessons)
James Madison Lesson 1: Madison Was There

Why is James Madison such an important figure? Why is he known as the “Father of the Constitution”? How involved was James Madison in the most important events in America from 1775 to 1817? The answers to these questions provide context for understanding the importance of James Madison’s opinions on constitutional issues. They also should help students appreciate Madison’s position as a president embroiled in disputes over the meaning of the document he had inspired.
Dolley Madison Before James

This short video explores the early life of Dolley Madison. Born into the Virginia gentry, Dolley spent her formative years in Philadelphia where she was married, widowed, and lost one of her children in the yellow fever epidemic of 1793. Professor Catherine Allgor describes James Madison as “smitten” with the 25 year-old widow and speculates why Dolley married James.
James Madison and the First Amendment

This short video traces the evolution of Madison’s attitude towards the religious liberty guarantees of the First Amendment. Initially opposed to a Bill of Rights as both inappropriate and dangerous, Madison’s views changed as a result of political and philosophical considerations. Professor Jeffry Morrison emphasizes Madison’s belief that religion should play a vital but informal role in the life of the republic.
James Madison in the 1780s
This short video explores the impact of James Madison’s experiences in both the Continental Congress and the Virginia House of Delegates in shaping his views of government. Madison understood the nature of collective deliberation and the Constitution reflects his interest in and understanding of the legislative process. Professor Jack Rakove examines Madison’s concerns about the “passions and interests” of both citizens and legislative bodies.
James Madison and the Constitution

This video highlights James Madison’s talents both as a creative thinker as well as someone with practical experiences in governing. Madison was the longest-lived of the Founding generation and had years after ratification to think about what it takes to make a Constitution work. Professor Jack Rakove notes that Madison lived long enough to hear questions raised about the Constitution’s origins (we, the people? Or we, the states?) and to anticipate the dissolution of the union he created.
Dolley Madison and Constitutional Thinking

This short video assesses the role played by Dolley Madison in promoting the experiment in republican government set in motion by the Constitution. She fully appreciated the 18th century idea of “manners”; i.e. how we treat each other is important. Professor Catherine Allgor contends that, when it came to manners, “women held the whole thing together” and Dolley’s contribution was invaluable as the young nation worked out constitutional precepts in practice.
Dolley Madison and Politics
This short video analyzes both the practical and the psychological contributions made by Dolley Madison to the young republic. Practically, Dolley’s weekly receptions in the drawing room of the White House became the only public gathering place in Washington, DC for doing the real business of politics. Psychologically, Dolley became, in the words of Professor Catherine Allgor, a “Republican Queen”, whose charm and charisma made her a symbol of America during the War of 1812.
Dolley Madison as First Lady

This short video emphasizes the importance of the unofficial sphere of the political world (the homes, social events, and private spaces where people gathered) and the role played by Dolley Madison in shaping this sphere. Professor Catherine Allgor concludes that Dolley, through this unofficial sphere, was the “queen” of influence peddling, using her status and connections to help staff the federal government.
Dolley Madison and Slavery
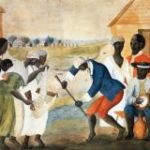
This short video presents Dolley Madison as a typical member of the antebellum slaveholding gentry. Dolley, like her southern contemporaries, saw slaves as property. Professor Catherine Allgor notes that when Dolley Madison began selling her slaves in the 1840’s, she was strongly criticized by the abolitionist press.